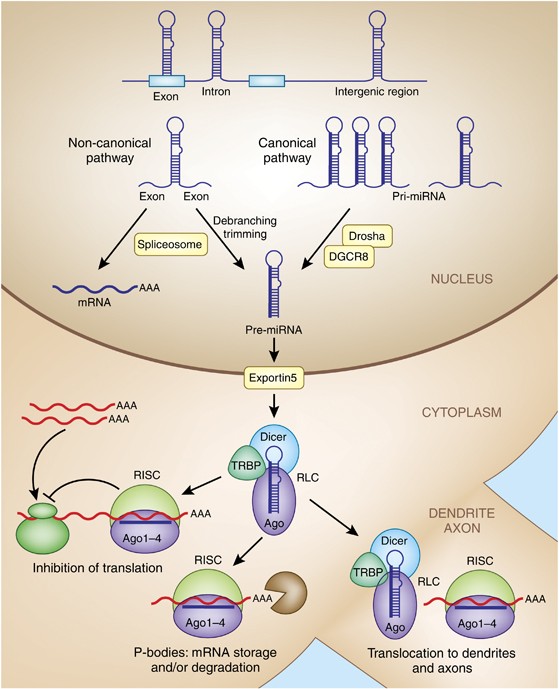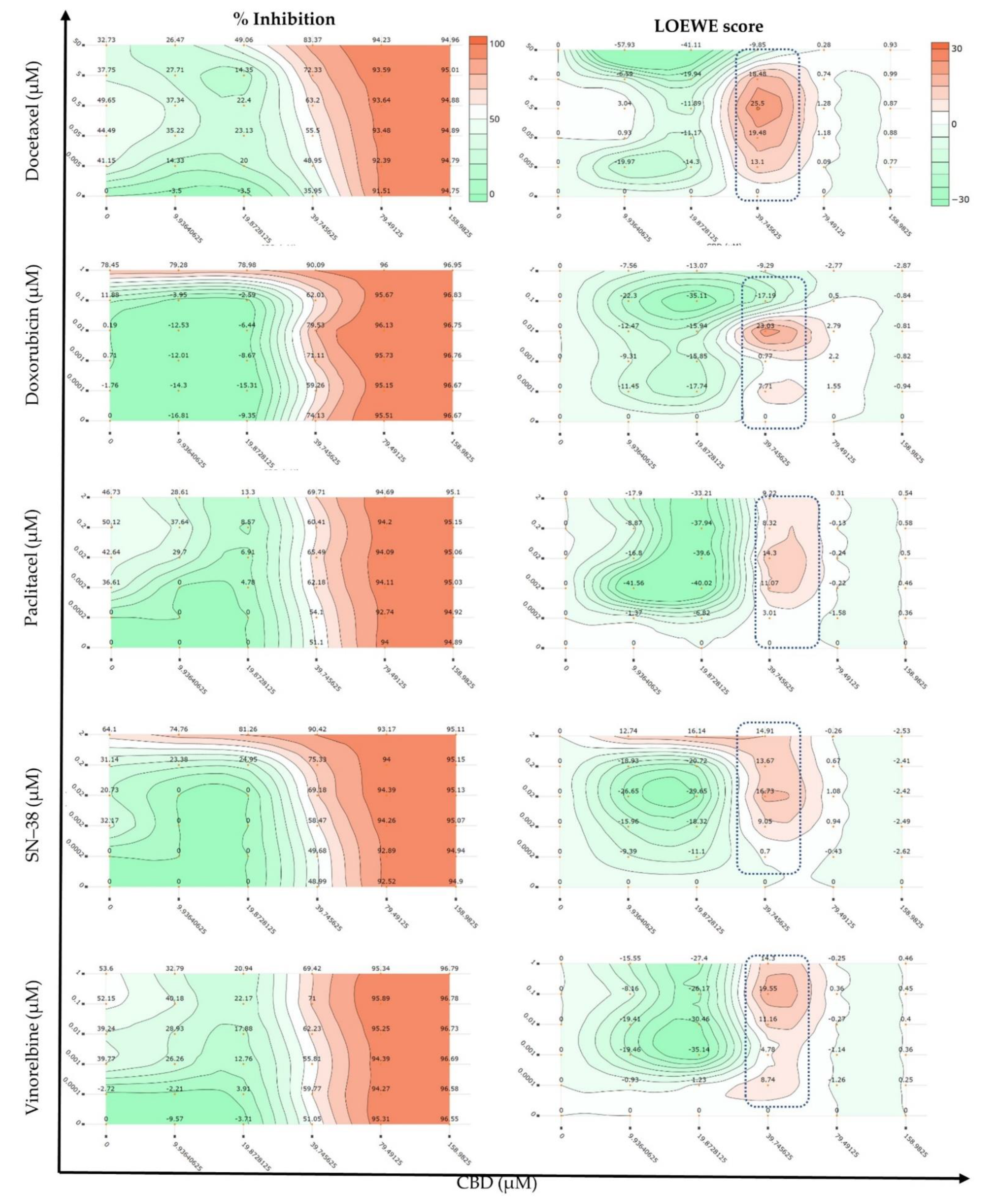
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Synergistic Interactions of Cannabidiol with Chemotherapeutic Drugs in MCF7 Cells: Mode of Interaction and Proteomics Analysis of Mechanisms

An Autocrine Lactate Loop Mediates Insulin-Dependent Inhibition of Lipolysis through GPR81 - ScienceDirect

The XPB Subunit of the TFIIH Complex Plays a Critical Role in HIV-1 Transcription, and XPB Inhibition by Spironolactone Prevents HIV-1 Reactivation from Latency | Journal of Virology
Elevated glucose represses lysosomal and mTOR-related genes in renal epithelial cells composed of progenitor CD133+ cells | PLOS ONE

The Anti-Inflammatory Agent Bindarit Attenuates the Impairment of Neural Development through Suppression of Microglial Activation in a Neonatal Hydrocephalus Mouse Model | Journal of Neuroscience

Multiplexed Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of HEK293 Provides Insights into Molecular Changes Associated with the Cell Density Effect, Transient Transfection, and Virus-Like Particle Production | Journal of Proteome Research
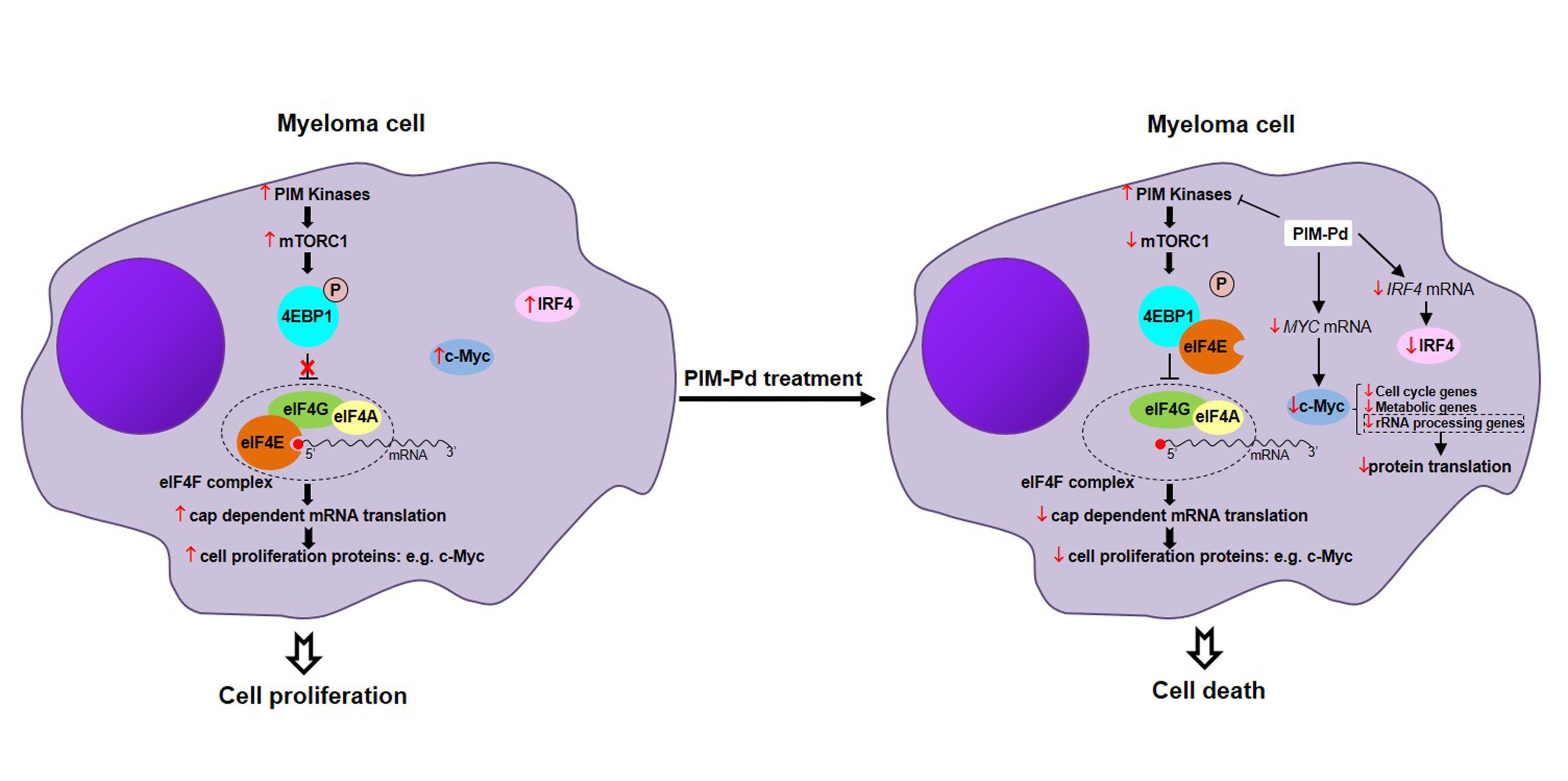
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Protein Translation Inhibition is Involved in the Activity of the Pan-PIM Kinase Inhibitor PIM447 in Combination with Pomalidomide-Dexamethasone in Multiple Myeloma

The XPB Subunit of the TFIIH Complex Plays a Critical Role in HIV-1 Transcription, and XPB Inhibition by Spironolactone Prevents HIV-1 Reactivation from Latency | Journal of Virology

The XPB Subunit of the TFIIH Complex Plays a Critical Role in HIV-1 Transcription, and XPB Inhibition by Spironolactone Prevents HIV-1 Reactivation from Latency | Journal of Virology

RBP EIF2S2 Promotes Tumorigenesis and Progression by Regulating MYC-Mediated Inhibition via FHIT-Related Enhancers: Molecular Therapy
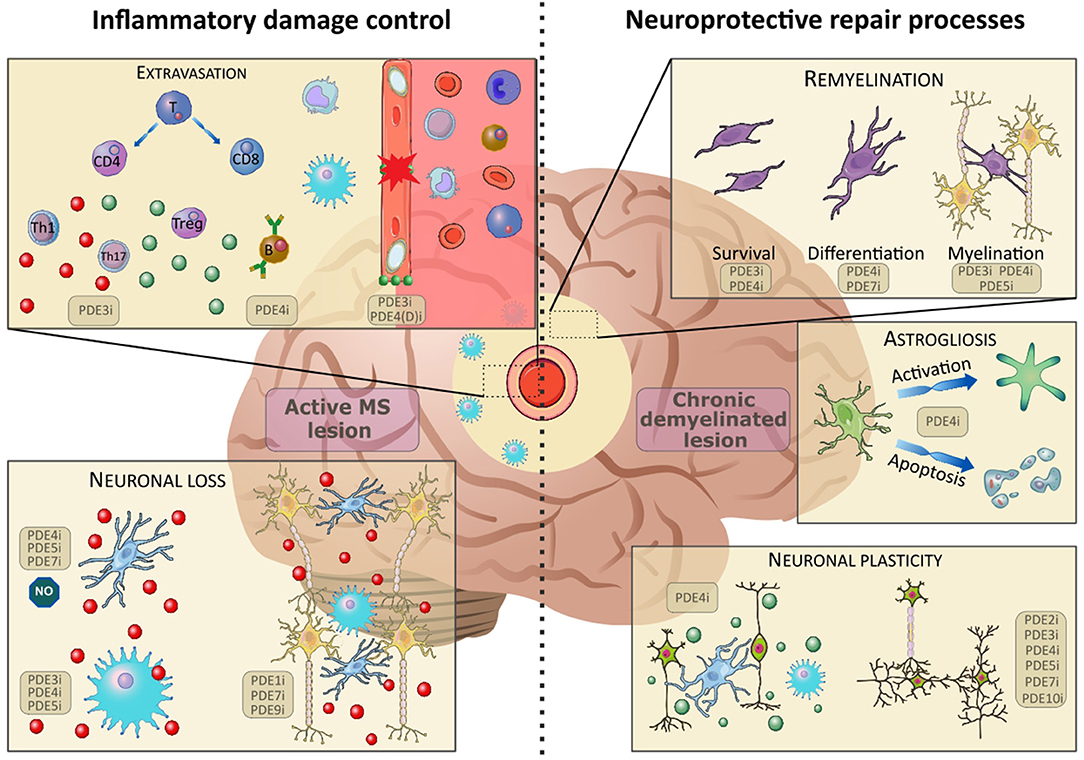
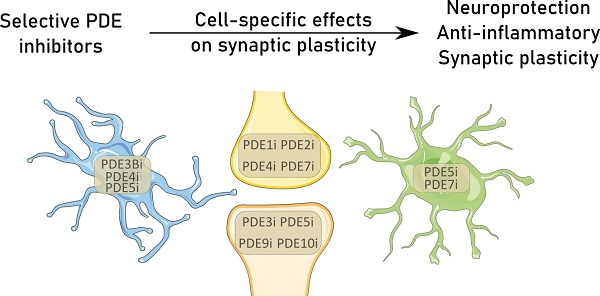
Frontiers | Targeting Phosphodiesterases—Towards a Tailor-Made Approach in Multiple Sclerosis Treatment

Exploring Methods of Targeting Histone Methyltransferases and Their Applications in Cancer Therapeutics | ACS Chemical Biology